Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In Ampere's \[\oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 i,\] the current outside the curve is not included on the right hand side. Does it mean that the magnetic field B calculated by using Ampere's law, gives the contribution of only the currents crossing the area bounded by the curve?
Solution
In Ampere's law \[\oint \vec{B} . \vec{dl} = \mu_o i\] , i is the total current crossing the area bounded by the closed curve. The magnetic field B on the left-hand side is the resultant field due to all existing currents.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write Maxwell's generalization of Ampere's circuital law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is `I=varepsilon_0 (dphi_E)/dt,`where ΦE is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T. What is the magnetic force on the wire?
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
A long, straight wire carries a current. Is Ampere's law valid for a loop that does not enclose the wire, or that encloses the wire but is not circular?
A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field
(a) increases linearly from the axis to the surface
(b) is constant inside the tube
(c) is zero at the axis
(d) is zero just outside the tube.
In a coaxial, straight cable, the central conductor and the outer conductor carry equal currents in opposite directions. The magnetic field is zero
(a) outside the cable
(b) inside the inner conductor
(c) inside the outer conductor
(d) in between the tow conductors.
A long, cylindrical tube of inner and outer radii a and b carries a current i distributed uniformly over its cross section. Find the magnitude of the magnitude filed at a point (a) just inside the tube (b) just outside the tube.
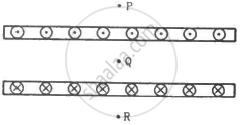
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
Using Ampere's circuital law, obtain an expression for the magnetic flux density 'B' at a point 'X' at a perpendicular distance 'r' from a long current-carrying conductor.
(Statement of the law is not required).
What is magnetic permeability?
Find the magnetic field due to a long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital law.
A straight wire of diameter 0.5 mm carrying a current of 1 A is replaced by another wire of 1 mm diameter carrying the same current. The strength of the magnetic field far away is ______.
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, then which statement is correct?
A solenoid of length 0.6 m has a radius of 2 cm and is made up of 600 turns If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is:
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
Consider the experimental set-up shown in the figure. This jumping ring experiment is an outstanding demonstration of some simple laws of Physics. A conducting non-magnetic ring is placed over the vertical core of a solenoid. When current is passed through the solenoid, the ring is thrown off. |
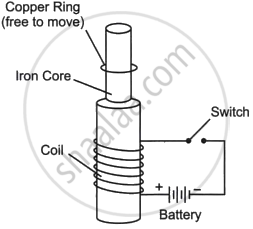
- Explain the reason for the jumping of the ring when the switch is closed in the circuit.
- What will happen if the terminals of the battery are reversed and the switch is closed? Explain.
- Explain the two laws that help us understand this phenomenon.
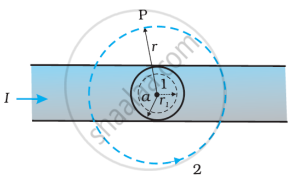
The given figure shows a long straight wire of a circular cross-section (radius a) carrying steady current I. The current I is uniformly distributed across this cross-section. Calculate the magnetic field in the region r < a and r > a.
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
