Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of different colours using diffraction grating.
Solution
- When white light is used, the diffraction pattern consists of a white central maximum and on both sides, continuous coloured diffraction patterns are formed.
- The central maximum is white as all the colours meet here constructively with no path difference. As θ increases, the path difference, (a+b)sin θ, passes through the condition for maxima of diffraction of different orders for all colours from violet to red.
- It produces a spectrum of the diffraction pattern from violet to red on either side of the central maximum
- By measuring the angle at which these colours appear for various orders of diffraction, the wavelength of different colours could be calculated using the formula,
`lambda = (sin theta)/"Nm"`
Here, N is the number of rulings per metre in the grating and m is the order of the diffraction image.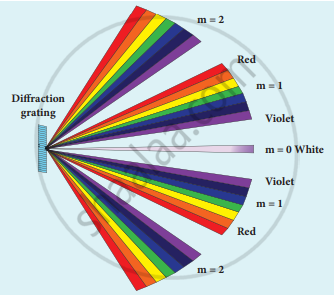
Diffraction with white light
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 4I are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are ______.
First diffraction minimum due to a single slit of width 1.0 × 10-5 cm is at 30°. Then wavelength of light used is ______.
What is diffraction?
Differentiate between Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction.
Mention the differences between interference and diffraction.
Discuss the special cases on first minimum in Fraunhofer diffraction.
What is Fresnel’s distance? Obtain the equation for Fresnel’s distance.
What is a diffraction grating?
What is Rayleigh’s criterion?
Discuss diffraction at single slit and obtain the condition for nth minimum.
Discuss the diffraction at a grating and obtain the condition for the mth maximum.
Discuss the experiment to determine the wavelength of monochromatic light using a diffraction grating.
Obtain the equation for resolving power of optical instrument
Light of wavelength of 5000 Å produces diffraction pattern of the single slit of width 2.5 μm. What is the maximum order of diffraction possible?
Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 104 A. The image seen through the slit shall ______.
Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103A. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be ______.
- a sharp white ring.
- different from a geometrical image.
- a diffused central spot, white in colour.
- diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot.
