Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
Solution
- The light from a clear blue portion of the sky shows a rise and fall of intensity when viewed through a polaroid that is rotated.
- This is because of sunlight, which has changed its I direction (having been scattered) on encountering the molecules of the earth’s atmosphere.
- The electric field of light interacts with the electrons present in the air molecules.
- Under the influence of the electric field of the incident wave the electrons in the molecules acquire components of motion in both these directions.
- We have an observer looking at 90° to the direction of the sun. Clearly, charges accelerating parallel do not radiate energy towards this observer since their acceleration has no transverse component.
- The radiation scattered by the molecule is therefore polarized perpendicular to the plane.

Polarisation by scattering
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
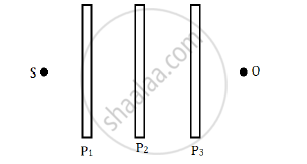
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Greenlight is an incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30°.
Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
What is plane polarised light?
What is partially polarised light?
State Brewster’s law.
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
What is normal focusing?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
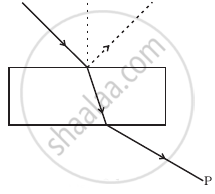
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
