Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss about Nicol prism.
Solution
Principle: Double Refraction
Construction:
- One of the most common forms of the Nicol prism is made by taking a calcite crystal which is a double refracting crystal with its length three times its breadth.
- It is cut into two halves along the diagonal so that their face angles are 72° and 108°.
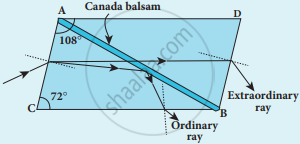
Nicol Prism - The two halves are joined together by a layer of Canada balsam, a transparent cement.
- A ray of unpolarized light from a monochromatic source such as a sodium vapour lamp is incident on the face AC of the Nicol prism. Double refraction takes place and the ray is split into ordinary and extraordinary rays.
- They travel with different velocities.
- The refractive index of the crystal for the ordinary ray (monochromatic sodium light) is 1.658 and for the extraordinary ray is 1.486. The refractive index of Canada balsam is 1.523.
- Canada balsam does not polarise light.
- The ordinary ray is total internally reflected at the layer of Canada balsam and is prevented from emerging from the other face.
- The extraordinary ray alone is transmitted through the crystal which is plane polarised.
-
Uses of Nicol prism:
- It produces plane polarised light and functions as a polariser
- It can also be used to analyse the plane polarised light (i.e) used as an analyser.
-
Drawbacks of Nicol prism:
- Its cost is very high due to the scarcity of large and flawless calcite crystals
- Due to an extraordinary ray passing obliquely through it, the emergent ray is always displaced a little to one side.
- The effective field of view is quite limited
- Light emerging out of it is not uniformly plane polarised.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
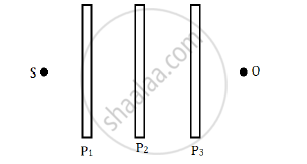
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
What dose a polaroid consist of?
Show, using a simple polaroid, that light waves are transverse in nature. Intensity of light coming out of a polaroid does not change irrespective of the orientation of the pass axis of the polaroid. Explain why.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
What is polarisation?
What is a analyser?
What is unpolarised light?
What is double refraction?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
