Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss about Nicol prism.
उत्तर
Principle: Double Refraction
Construction:
- One of the most common forms of the Nicol prism is made by taking a calcite crystal which is a double refracting crystal with its length three times its breadth.
- It is cut into two halves along the diagonal so that their face angles are 72° and 108°.
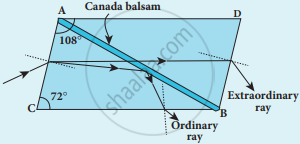
Nicol Prism - The two halves are joined together by a layer of Canada balsam, a transparent cement.
- A ray of unpolarized light from a monochromatic source such as a sodium vapour lamp is incident on the face AC of the Nicol prism. Double refraction takes place and the ray is split into ordinary and extraordinary rays.
- They travel with different velocities.
- The refractive index of the crystal for the ordinary ray (monochromatic sodium light) is 1.658 and for the extraordinary ray is 1.486. The refractive index of Canada balsam is 1.523.
- Canada balsam does not polarise light.
- The ordinary ray is total internally reflected at the layer of Canada balsam and is prevented from emerging from the other face.
- The extraordinary ray alone is transmitted through the crystal which is plane polarised.
-
Uses of Nicol prism:
- It produces plane polarised light and functions as a polariser
- It can also be used to analyse the plane polarised light (i.e) used as an analyser.
-
Drawbacks of Nicol prism:
- Its cost is very high due to the scarcity of large and flawless calcite crystals
- Due to an extraordinary ray passing obliquely through it, the emergent ray is always displaced a little to one side.
- The effective field of view is quite limited
- Light emerging out of it is not uniformly plane polarised.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
What is a Polaroid?
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 45° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
State two uses of Polaroid.
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
What is plane polarised light?
What is partially polarised light?
State Brewster’s law.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
Discuss about pile of plates.
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
What is normal focusing?
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
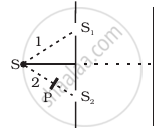
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
