Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two uses of Polaroid.
उत्तर
Uses of Polaroid:-
(1) In motor car head lights – To remove headlight glare
(2) To improve color contrast in old oil paintings
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
Show, using a simple polaroid, that light waves are transverse in nature. Intensity of light coming out of a polaroid does not change irrespective of the orientation of the pass axis of the polaroid. Explain why.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 45° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
What is polarisation?
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is plane polarised light?
What is double refraction?
Discuss about Nicol prism.
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
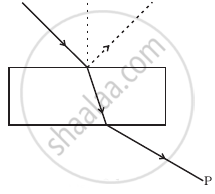
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
