Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
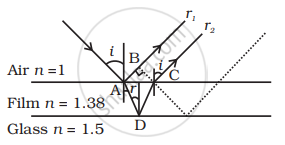
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
उत्तर
Consider a ray incident at an angle i. A part of this ray is reflected from the air-film interface and a part is refracted inside. This is partly reflected at the film-glass interface and a part transmitted. A part of the reflected ray is reflected at the film-air interface and a part is transmitted as r2 parallel to r1. Of course, successive reflections and transmissions will keep on decreasing the amplitude of the wave. Hence rays r1 and r2 shall dominate the behaviour. If the incident light is to be transmitted through the lens, r1 and r2 should interfere destructively. Both the reflections at A and D are from lower to higher refractive index and hence there is no phase change on reflection. The optical path difference between r2 and r1 is n (AD + CD) – AB.
If d is the thickness of the film, then
`AD = CD = d/cos r`
`AB = AC sin i`
`(AC)/2` = d tan r
∴ `AC = 2d tan r`
Hence, `AB = 2d tanr sini`
Thus the optical path difference is
`2n d/cos r - 2d tan r sin i`
= `2. sin i/sin r d/cos r - 2d sinr/cos r sin i`
= `2d sin [(1 - sin^2r)/(sinr cos r)]`
= `2 nd cos r`
For these waves to interfere destructively this must be `λ/2`.
⇒ `2nd cos r = λ/2`
or `nd cos r = λ/4`
For a camera lens, the sources are in the vertical plane and hence `i ≃ r ≃ 0`
∴ `nd ≃ λ/4`
⇒ `d = (5500 Å)/(1.38 xx 4) ≃ 1000 Å`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
What is a polariser?
What is a analyser?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
