Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
उत्तर
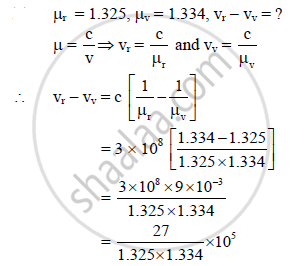
= [log (27) − log (1.325) − log (1.334)] × 105
= [1.4314 − 0.1222 − 0.1252] × 105
= [antilog (1.184)] × 105
= 15.28 × 105 = 1.528 × 106 m/s.
The difference between the velocities of rays for red and violet colours in water is
1.528 × 106 m/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a Polaroid?
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum?
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a analyser?
What is plane polarised light?
What is partially polarised light?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
Discuss about Nicol prism.
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
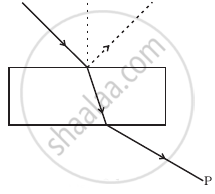
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
