Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
उत्तर

If a dielectric (non-polar) molecule is placed in an external electric field, a small induced dipole moment is created because the positive charge in each atom is pushed in the direction of the field and negative charge is pushed in the opposite direction as shown in the figure.
Polarization is the amount of induced surface charge per unit area or the surface density of polarization charges appearing at right angles to applied external electric field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60°?
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
What is a polariser?
What is a analyser?
What is plane polarised light?
List the uses of polaroids.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
What is double refraction?
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
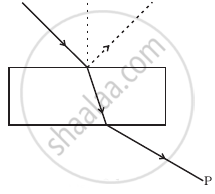
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
