Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
विकल्प
interference
diffraction
scattering
polarisation
उत्तर
The transverse nature of light is shown in polarisation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
State two uses of Polaroid.
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Greenlight is an incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30°.
Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
State and obtain Malus’ law.
Discuss about pile of plates.
What is normal focusing?
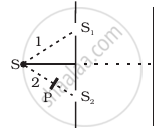
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.