Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
उत्तर

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
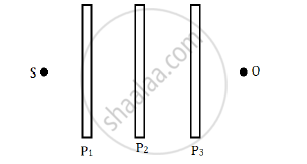
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
State two uses of Polaroid.
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
What is polarisation?
What is a polariser?
What is a analyser?
What is unpolarised light?
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
Discuss about pile of plates.
What is double refraction?
What is normal focusing?
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
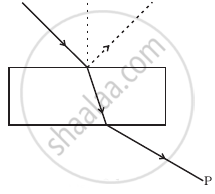
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
