Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is unpolarised light?
उत्तर
A transverse wave that has vibrations in all directions in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation is said to be unpolarised light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
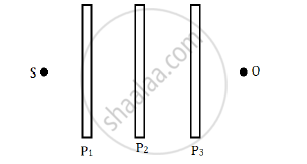
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 45° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
State two uses of Polaroid.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a analyser?
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
Discuss about pile of plates.
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
