Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
उत्तर
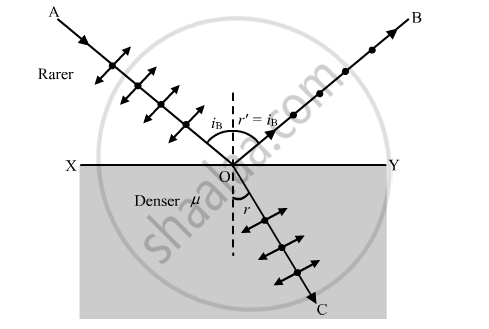
When unpolarised light is incident on the glass-air interface at Brewster angle iB, then reflected light is totally polarised. This is called Brewster's Law.
When light is incident at Brewster angle, the reflected component OB and the refracted component OC are mutually perpendicular to each other.
From the figure, we have
∠BOY + ∠YOC = 900
( 900 − iB ) + ( 900 − r ) = 900
where, r is angle of refraction
900 − iB = r
According to the Snell's law:
`mu=sini/sinr`
i = iB and r = (900 − iB)
`mu=sini_B/sin(90^@-i_B)=sini_B/cosi_B`
μ =tan iB
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
State and obtain Malus’ law.
List the uses of polaroids.
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
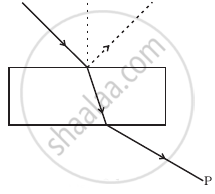
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.