Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe a simple experiment (or activity) to show that the polarity of emf induced in a coil is always such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change of magnetic flux that produces it.
उत्तर
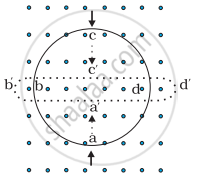
Lenz law: According to Lenz's law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it opposes a change in magnetic flux responsible for its production.
Activity:

When the north pole of a bar magnet is pushed towards the coil, the amount of magnetic flux linked with the coil increases. Current is induced in the coil in from a direction such that it opposes the increase in magnetic flux. This is possible only when the current induced in the coil is in anti-clockwise direction, with respect to an observer. The magnetic moment `vecM` associated with this induced emf has north polarity, towards the north pole of the approaching bar magnet.
Similarly, when the north pole of the bar magnet is moved away from the coil, the magnetic flux linked with the coil decreases. To counter this decrease in magnetic flux, current is induced in the coil in clockwise direction so that its south pole faces the receding north pole of the bar magnet. This would result in an attractive force which opposes the motion of the magnet and the corresponding decrease in magnetic flux.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
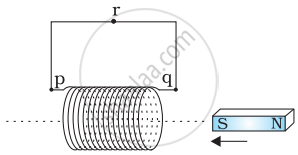
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
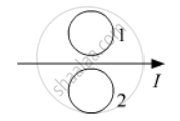
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
A pivoted aluminium bar falls much more slowly through a small region containing a magnetic field than a similar bar of an insulating material. Explain.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A bar magnet is dropped through a copper ring acceleration of magnet is
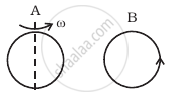
Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is ______.
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a carboard) (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain
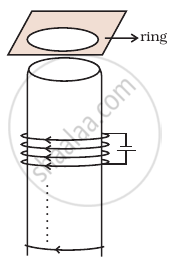
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure.
A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.