Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
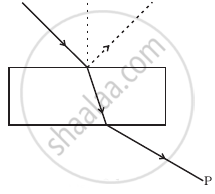
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
विकल्प
For a particular orientation there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid.
The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation.
The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go through a minimum for four orientations of the polaroid.
उत्तर
The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
Explanation:
Brewster discovered that when a beam of unpolarised light is reflected from a transparent medium (refractive index = µ), the reflected light is completely plane polarised at a certain angle of incidence (called the angle of polarisation θp).
From figure, it is clear that θp+ θr = 90°
Also n = tan θp ......(Brewster’s law)
(i) For i < θp or i > θp
Both reflected and refracted rays become partially polarised.
(ii) For glass θp = 51° for water θp = 53°
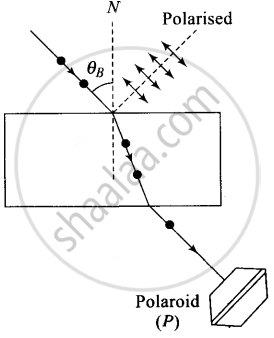
If a light beam is incident on a glass slab at Brewster’s angle, the transmitted beaiji is unpolarised and reflected beam is polarised.
In the given figure, the light beam is incident from air to the glass slab at Brewster’s angle (ip). The incident ray is unpolarised and is represented by dot (•). The reflected light is plane polarised represented by arrows. As the emergent ray is unpolarised, hence intensity cannot be zero when passes through the polaroid.
Important points:
Polarised light: The phenomenon of limiting the vibrating of electric field vector in one direction in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light wave is called polarization of light.
- The plane in which oscillation occurs in the polarised light is called plane of oscillation.
- The plane perpendicular to the plane of oscillation is called plane of polarisation.
- Light can be polarised by transmitting through certain crystals such as tourmaline or polaroids.
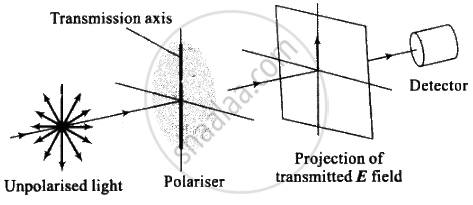
Polaroids: It is a device used to produce the plane polarised light. It is based on the principle of selective absorption and is more effective than the tourmaline crystal, or it is a thin film of ultramicroscopic crystals of quinine iodosulphate with their optic axis parallel to each other.
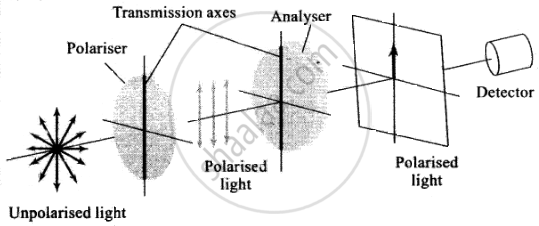
(A) Transmission axes of the polariser and analyser are parallel to each other, so whole of the polarised light passes through analyser
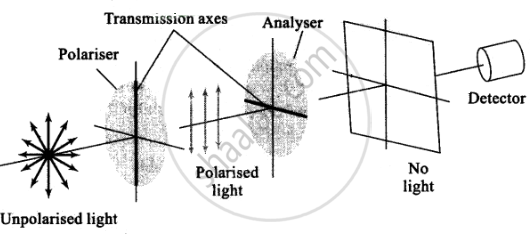
(B) Transmission axis of the analyser is perpendicular to the polariser, hence no light passes through the analyser
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
Discuss about pile of plates.
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
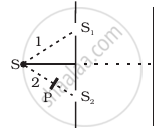
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.