Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
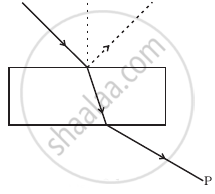
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
पर्याय
For a particular orientation there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid.
The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation.
The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go through a minimum for four orientations of the polaroid.
उत्तर
The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
Explanation:
Brewster discovered that when a beam of unpolarised light is reflected from a transparent medium (refractive index = µ), the reflected light is completely plane polarised at a certain angle of incidence (called the angle of polarisation θp).
From figure, it is clear that θp+ θr = 90°
Also n = tan θp ......(Brewster’s law)
(i) For i < θp or i > θp
Both reflected and refracted rays become partially polarised.
(ii) For glass θp = 51° for water θp = 53°
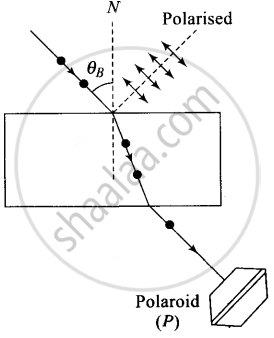
If a light beam is incident on a glass slab at Brewster’s angle, the transmitted beaiji is unpolarised and reflected beam is polarised.
In the given figure, the light beam is incident from air to the glass slab at Brewster’s angle (ip). The incident ray is unpolarised and is represented by dot (•). The reflected light is plane polarised represented by arrows. As the emergent ray is unpolarised, hence intensity cannot be zero when passes through the polaroid.
Important points:
Polarised light: The phenomenon of limiting the vibrating of electric field vector in one direction in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light wave is called polarization of light.
- The plane in which oscillation occurs in the polarised light is called plane of oscillation.
- The plane perpendicular to the plane of oscillation is called plane of polarisation.
- Light can be polarised by transmitting through certain crystals such as tourmaline or polaroids.
Polaroids: It is a device used to produce the plane polarised light. It is based on the principle of selective absorption and is more effective than the tourmaline crystal, or it is a thin film of ultramicroscopic crystals of quinine iodosulphate with their optic axis parallel to each other.
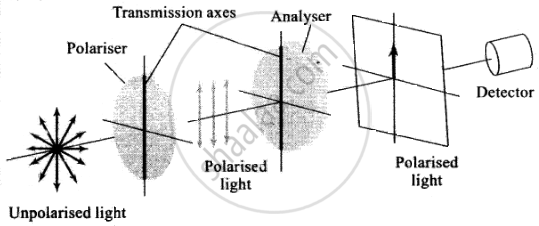
(A) Transmission axes of the polariser and analyser are parallel to each other, so whole of the polarised light passes through analyser
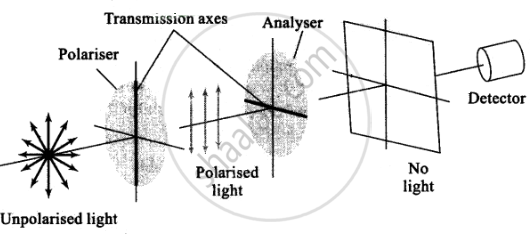
(B) Transmission axis of the analyser is perpendicular to the polariser, hence no light passes through the analyser
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
What is a Polaroid?
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
List the uses of polaroids.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of light coming out of the analyser is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser need to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero, is ______.
