Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is a Polaroid?
उत्तर
A Polaroid is a material which polarises light. The phenomenon of selective absorption is made use of in the construction of polariods. There are different types of polaroids.
A Polaroid consists of micro crystals of herapathite (an iodosulphate of quinine). Each crystal is a doubly refracting medium, which absorbs the ordinary ray and transmits only the extra ordinary ray. The modern polaroid consists of a large number of ultra microscopic crystals of herapathite embedded with their optic axes, parallel, in a matrix of nitro - cellulose.
Recently, new types of polariod are prepared in which thin film of polyvinyl alcohol is used. These are colourless crystals which transmit more light, and give better polarisation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
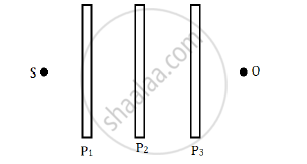
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60°?
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a polariser?
What is plane polarised light?
State and obtain Malus’ law.
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
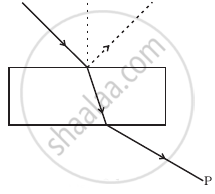
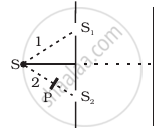
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of light coming out of the analyser is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser need to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero, is ______.
