Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
उत्तर
As given in the question, the polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Also, polaroid P3 is placed at an angle of 30° with respect to P1.
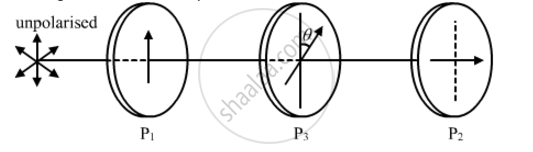
Now, we have:
Intensity of light after falling on P1 `I'=I_0/2`
Intensity of light after falling on P3, I" =
`I'cos^2(theta)=I_0/2cos^2(30^@)=(3I_0)/8`
Therefore, a light of intensity `(3I_0)/8`will pass through the P3, and the angle between P3 and P2 will be 60° because of the condition given in the question.
Intensity of light after falling on P2, I"' = I" `cos^2(theta)=(3I_0)/8cos^2(60^@)=(3I_0)/32`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
What is polarisation?
List the uses of polaroids.
State Brewster’s law.
What is double refraction?
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.