Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
उत्तर
A polaroid consists of long-chain molecules aligned in a particular direction. The electric vectors (associated with the propagating light wave) along the direction of the aligned molecules get absorbed. Thus, if an unpolarised light wave is incident on such a polaroid, then the light wave will get linearly polarised with the electric vector oscillating along a direction perpendicular to the aligned molecule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a Polaroid?
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
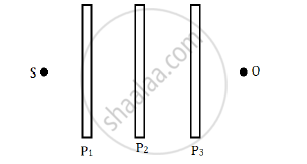
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Discuss about pile of plates.
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
