Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
उत्तर

The phenomenon of restricting the vibration of light (electric vector) in a particular direction perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation is called polarisation of light.
When unpolarised light is passed through a Polaroid, only those vibrations of light pass through the crystal, which are parallel to the axis of the crystal (AB). All other vibrations are absorbed and that is why intensity of the emerging light is reduced.
The plane ABCD in which the vibrations of the polarised light are confined is called the plane of vibration. The plane KLMN that is perpendicular to the plane of vibration is defined as the plane of polarisation
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
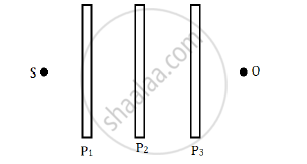
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
What dose a polaroid consist of?
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
What is normal focusing?
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
