Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
उत्तर
If angle of incidence is equal to Brewster’s angle, the transmitted light is slightly polarised and reflected light is plane polarised.
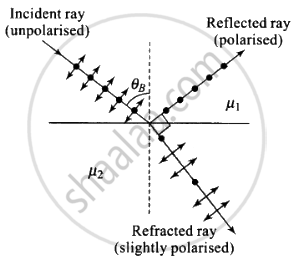
Polarisation by reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is Brewster's angle.
i.e., `tan i_B = ""^1mu_2 = mu_2/mu_1` where `mu_2 < mu_1`
When the light rays travel in such a medium, the critical angle is
`sin i_C = mu_2/mu_1`, where `mu_2 < mu_1`
As `|tan i_B| > |sin i_C|` for large angles `i_B < i_C`
Thus, the polarisation by reflection occurs definitely.
Important point: Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
What is double refraction?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
