Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
उत्तर
If angle of incidence is equal to Brewster’s angle, the transmitted light is slightly polarised and reflected light is plane polarised.
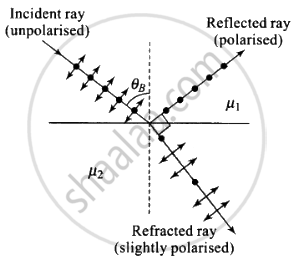
Polarisation by reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is Brewster's angle.
i.e., `tan i_B = ""^1mu_2 = mu_2/mu_1` where `mu_2 < mu_1`
When the light rays travel in such a medium, the critical angle is
`sin i_C = mu_2/mu_1`, where `mu_2 < mu_1`
As `|tan i_B| > |sin i_C|` for large angles `i_B < i_C`
Thus, the polarisation by reflection occurs definitely.
Important point: Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
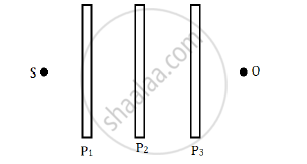
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
What is polarisation?
What is partially polarised light?
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
