Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
उत्तर
For i = 2r
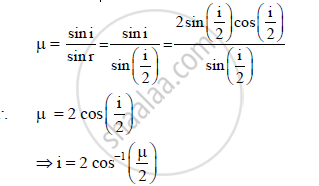
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
State two uses of Polaroid.
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
The transverse nature of light is shown in ______.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a analyser?
What is partially polarised light?
What is double refraction?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
Discuss about Nicol prism.
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
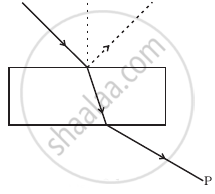
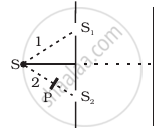
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of light coming out of the analyser is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser need to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero, is ______.
