Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
Solution
For i = 2r
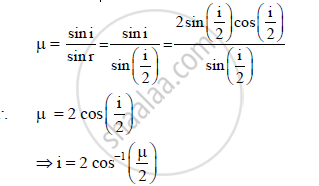
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
What is a Polaroid?
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane of polarisation for polarised light.
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
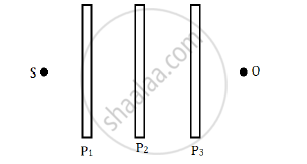
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum?
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Greenlight is an incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30°.
Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a analyser?
List the uses of polaroids.
What is double refraction?
What is normal focusing?
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
