Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
उत्तर
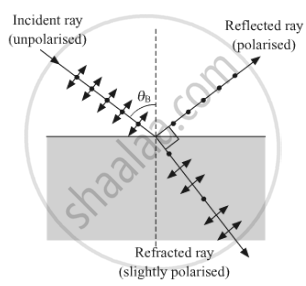
When an unpolarized light falls on the interface separating two transparent media, mostly only those electric vectors get reflected at the boundary which is oscillating along a direction perpendicular to the plane of incidence, hence the reflected ray will be polarised containing only electric vectors. The complete polarisation takes place when the reflected wave and the refracted wave are perpendicular to each other.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 45° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
State two uses of Polaroid.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
What is a analyser?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
What is normal focusing?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
