Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is a analyser?
उत्तर
The polaroid which is used to examine whether a beam of light is polarised or not is called an analyser.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Using the phenomenon of polarisation, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
State two uses of Polaroid.
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
What is polarisation?
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
State and obtain Malus’ law.
List the uses of polaroids.
What is normal focusing?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
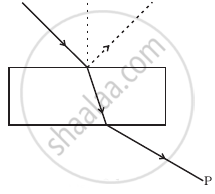
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.