Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
उत्तर
χ = 4224
∴ μ = μ0 (1 + χ)
= 4π × 10−7 (1 + 4224)
= 16900 π × 10−7
= 169 × 3.142 × 10−5
= [log (169) + log (3.142)] × 10−5
= [2.2279 + 0.4972] × 10−5
= antilog (2.7251)] × 10−5
= 531 × 10−5
= 5.31 × 10−3 Hm−1
The permeability of annealed iron at saturation is 5.31 × 10−3 Hm−1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
What happens to a ferromagnetic material when its temperature increases above curie temperature?
Answer in brief.
Discuss the Curie law for paramagnetic material.
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is χ at 27° C. At what temperature its susceptibility be χ/3?
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is positive and small. The material is ______.
Magnetic material can be easily magnetized if magnetic susceptibility is ______.
There are three needles 'N1', 'N2' and 'N3' made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. When a magnet is brought close to them, then it will ____________.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
A sphere of gold when brought towards a powerful magnet experiences ____________.
A small quantity of paramagnetic liquid is taken in a watch - glass and kept on two dissimilar magnetic poles. The liquid ____________.
The earth’s field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30,000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion?
Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
Nickel shows ferromagnetic property at room temperature. If the temperature is increased beyond curie temperature, then it will show ______.
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
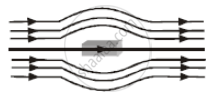
Assertion: A paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetic field) when cooled.
Reason: The magnetisation does not depend on temperature.
The magnetic susceptibility is negative for ______.
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
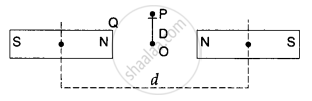
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
For a diamagnetic material
If a charged particle at rest experience no electromagnetic force
The universal property of all substances is ______.
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am–1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be ______.
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10–9) (at STP) and Cu (~10–5).
An ammeter of resistance R gives a full-scale deflection when a current of 2 A passes through it. If it is measured with a maximum current of 10 A, the required shunt is ______.
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
The relative magnetic permeability of a substance X is slightly less than unity and that of substance Y is slightly more than unity, then ______.
What is magnetic hysterisis?
Explain the origin of paramagnetism on the basis of atomic structure.
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance ______.
