Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
उत्तर
When unpolarised light passes through the polariser P1 the intensity drops to half that is `I_o/2` and when this polarised light passes through the polariser P2 the instensity of the emitted light is
`I=I_0/2cos^2 theta`
(θ is the angle between polariser P1 and P2)
The instensity distrubution is as shown below:

संबंधित प्रश्न
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
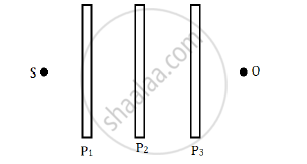
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
What is a analyser?
What is partially polarised light?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
