Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
Solution
When unpolarised light passes through the polariser P1 the intensity drops to half that is `I_o/2` and when this polarised light passes through the polariser P2 the instensity of the emitted light is
`I=I_0/2cos^2 theta`
(θ is the angle between polariser P1 and P2)
The instensity distrubution is as shown below:

RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
What is polarisation?
What is unpolarised light?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
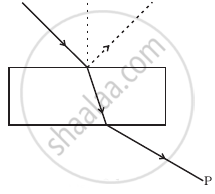
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
