Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is plane polarised light?
उत्तर
If the vibrations of a wave are present in only one direction in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave is said to be polarised or plane polarised light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
What dose a polaroid consist of?
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
When a low flying aircraft passes overhead, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Suggest a possible explanation.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
State two uses of Polaroid.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a polariser?
What is a analyser?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
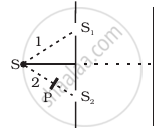
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of light coming out of the analyser is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser need to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero, is ______.
