Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum?
उत्तर

Let us consider two crossed polarisers P1 and P2, with a polaroid sheet P3 placed between them.
Let I0 be the intensity of polarised light after passing through the first polariser P1. If θ is the angle between the axes of P1 and P3, then the intensity of the polarised light after passing through P3 will be I=I0cos2θ.
As P1 and P2 are crossed, the angle between the axes of P1 and P2 = 90°.
∴ Angle between the axes of P2 and P3 = (90°−θ)
The intensity of light emerging from P2 will be given by
I=[I0cos2θ]cos2(90°−θ)
⇒I=[I0cos2θ]sin2θ
`=>I=I_0/4(4cos^2thetasin^2theta)`
`=>I=I_0/4(2sinthetacostheta^2)`
`=>I=I_0/4sin^2theta`
The intensity of polarised light transmitted from P2 will be maximum when
sin2θ=maximum=1
⇒sin2θ=sin90°
⇒2θ=90°
⇒θ=45°
Also, the maximum transmitted intensity will be given by
`I=I_0/4`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
Which of the following properties shows that light is a transverse wave?
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
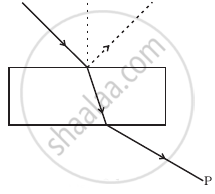
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
