Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
उत्तर
Given :
The critical angle is given as
sinθc = 1/n
`therefore theta_c=sin^-1(1/n)` ...(1)
It is given that
`theta_c=sin^-1(3/5)`
`therefore sin^-1(1/n)=sin^-1(3/5)` ...........form (1)
`therefore 1/n=3/5`
`therefore n=5/3`
Now, the polarising angle is given as
`theta_p=tan^-1 n`
`theta_p=tan^(-1)(5/3)`
`theta_p=tan^(-1)(1.667)`
`theta_p=59^@2'`
the polarising angle is `59^@2'`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the polarising angle for a given medium is 60°, then the refractive index of the medium is.................
What is a Polaroid?
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
What dose a polaroid consist of?
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
A ray of light passes from a vacuum to a medium of refractive index (μ). The angle of
incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. The angle of incidence is _______.
A) `cos^(-1)(mu/2)`
B) cos−1(μ)
C) `2 cos^(-1) (mu/2)`
D) `2 sin^(-1) (mu/2)`
What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60°?
State two uses of Polaroid.
State any two methods by which ordinary light can be polarised
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
What is a analyser?
What is plane polarised light?
What is double refraction?
What is normal focusing?
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
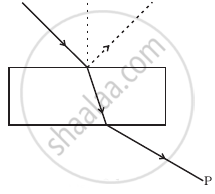
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
