Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State two uses of Polaroid.
Solution
Uses of Polaroid:-
(1) In motor car head lights – To remove headlight glare
(2) To improve color contrast in old oil paintings
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of neat diagram, explain how non-polar dielectric material is polarised in external electric field of increasing intensity. Define polarisation in dielectrics.
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
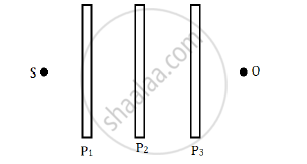
Three identical polaroid sheets P1, P2 and P3 are oriented so that the pass axis of P2 and P3 are inclined at angles of 60° and 90° respectively with the pass axis of P1. A monochromatic source S of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is kept in front of the polaroid sheet P1 as shown in the figure. Determine the intensities of light as observed by the observer at O, when polaroid P3 is rotated with respect to P2 at angles θ = 30° and 60°.
Show, using a simple polaroid, that light waves are transverse in nature. Intensity of light coming out of a polaroid does not change irrespective of the orientation of the pass axis of the polaroid. Explain why.
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60°?
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
Greenlight is an incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30°.
Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
What is a polariser?
State Brewster’s law.
What is double refraction?
Discuss about Nicol prism.
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
A plane mirror produces a magnification of
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
An unpolarized light beam is incident on the polarizer of a polarization experiment and the intensity of light beam emerging from the analyzer is measured as 100 Lumens. Now, if the analyzer is rotated around the horizontal axis (direction of light) by 30° in clockwise direction, the intensity of emerging light will be ______ Lumens.
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of light coming out of the analyser is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser need to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero, is ______.
