Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss about pile of plates.
Solution
- The phenomenon of polarisation by reflection is used in the construction of pile of plates.
- It consists of a number of glass plates placed one over the other in a tube
- The plates are inclined at an angle of 33.7°(90° – 56.3°) to the axis of the tube. A beam of unpolarised light is allowed to fall on the pile of plates along the axis of the tube. So, the angle of incidence of light will be at 56.3° which is the polarising angle for glass.
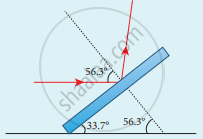
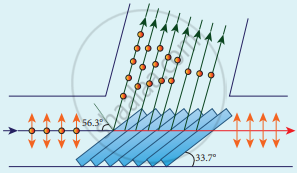
Pile of plates - The vibrations perpendicular to the plane of incidence are reflected at each surface and those parallel to it are transmitted.
- The larger the number of surfaces, the greater is the intensity of the reflected plane polarised light.
- The pile of plates is used as a polarizer and also as an analyser.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a Polaroid?
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum?
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
A beam of light is incident at the polarizing angle of 35° on a certain glass plate. The refractive index of the glass plate is :
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
What is a analyser?
What is partially polarised light?
State and obtain Malus’ law.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
Polarisation of light is the only phenomenon that establishes ______.
Which of the following phenomena is not common to sound and light waves?
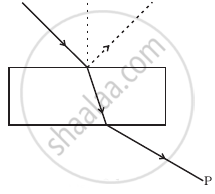
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.