Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The refractive indices of glass and water w.r.t. air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. Determine the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water.
Solution
Given:
`""_amu_g=3/2, ""_amu_w=4/3`
Find: `""_wmu_g`
Formula: `""_wmu_g=(""_amu_g)/(""_amu_w)`
solution: `""a_mu_g=C_a/C_g and ""_amu_w=C_a/C_w`
`""_wmu_g=C_w/C_g`
From Formula
`""_amu_g=(3/2)/(4/3)`
`""_wmu_g=1.12`
The refractive index of glass w.r.t. water is 1.12.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a glass plate as a polariser with refractive index 1.633, calculate the angle of incidence at which light is polarised.
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarised light when passed through a Polaroid gets polarised?
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Show, via a suitable diagram, how unpolarised light can be polarised by reflection.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are 1.325 and 1.334 respectively.
Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. (c = 3 × 108 m/s)
The glass plate of refractive index 1.732 is to be used as a polarizer, its polarising angle is _______.
With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam of light is polarised or unpolarized?
What does a polaroid consist of? How does it produce a linearly polarised light?
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
What is the difference between polarised light and unpolarised light?
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Greenlight is an incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30°.
Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
Discuss polarisation by selective absorption.
What is a polariser?
What is plane polarised light?
State Brewster’s law.
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain the equation for an angle of polarisation?
What is double refraction?
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
An unpolarised light of intensity 32 Wm-2 passes through three Polaroids such that the axes of the first and the last Polaroids are at 90°. What is the angle between the axes of the first and middle Polaroids so that the emerging light has an intensity of only 3 Wm-2?
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in figure. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
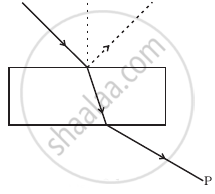
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance.
