Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
Solution
- When a ray of light passes through a glass slab it refracts at two refracting surfaces.
- When the light ray enters the slab it travels from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass), results in deviation of ray towards the normal. When the light ray leaves the slab it travels from denser medium to rarer medium resulting in deviation of ray away from the normal.

Refraction in glass slab - After the two refractions, the emerging ray has the same direction as that of the incident ray on the slab with a lateral displacement or shift L.
- Consider a glass slab of thickness and refractive index n is kept in air medium.
- In the right angle triangle ∆ BCE,
sin (i – r) = `"L"/"BC"`;
BC = `"L"/(sin ("i - r"))` ....(1) - In the right angle triangle ∆ BCF, ....(2)
cos(r) = `"t"/"BC"`;
BC = `"t"/(cos ("r"))`
Equating equations (1) & (2)
`"L"/(sin ("i - r")) = "t"/(cos ("r"))` - After rearranging,
L = `"t" [(sin ("i - r"))/(cos ("r"))]`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
How does an endoscope work?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
Light travels from an optically denser medium 'A' into the optically rarer medium 'B' with speeds 1.8 × 108 m/s and 2.7 × 108 m/s respectively. Then critical angle between them is ______.
(µ1 and µ2 are the refractive indices of media A and B respectively.)
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
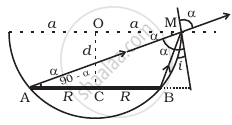
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?