Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
उत्तर
- When a ray of light passes through a glass slab it refracts at two refracting surfaces.
- When the light ray enters the slab it travels from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass), results in deviation of ray towards the normal. When the light ray leaves the slab it travels from denser medium to rarer medium resulting in deviation of ray away from the normal.

Refraction in glass slab - After the two refractions, the emerging ray has the same direction as that of the incident ray on the slab with a lateral displacement or shift L.
- Consider a glass slab of thickness and refractive index n is kept in air medium.
- In the right angle triangle ∆ BCE,
sin (i – r) = `"L"/"BC"`;
BC = `"L"/(sin ("i - r"))` ....(1) - In the right angle triangle ∆ BCF, ....(2)
cos(r) = `"t"/"BC"`;
BC = `"t"/(cos ("r"))`
Equating equations (1) & (2)
`"L"/(sin ("i - r")) = "t"/(cos ("r"))` - After rearranging,
L = `"t" [(sin ("i - r"))/(cos ("r"))]`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter?
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.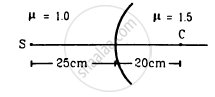
Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is a principle of reversibility?
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
