Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

उत्तर
Given,
Refractive index of water = μ.
Height of the pot = H
Let us take x as the distance of the image of the eye formed above the surface of the water as seen by the fish.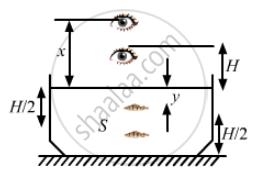
We can infer from from the diagram,
\[\frac{H}{x} = \frac{Real depth}{Apparent depth} = \frac{1}{\mu}\]
\[or x = \mu H\]
The distance of the direct image
\[= \frac{H}{2} + \mu H = H\left( \mu + \frac{1}{2} \right)\]
\[\frac{H}{x} = \frac{Real depth}{Apparent depth} = \frac{1}{\mu}\]
\[or x = \mu H\]
Similarly, image through mirror = \[\frac{H}{2} + (H + x) = \frac{3H}{2} + \mu H = H\left( \frac{3}{2} + \mu \right)\]
b) We know that:
\[\frac{H}{2} + (H + x) = \frac{3H}{2} + \mu H = H\left( \frac{3}{2} + \mu \right)\]
Where, y is the distance of the image of the fish below the surface as seen by the eye.
Direct image = \[H + y = H + \frac{H}{2\mu} = H\left( 1 + \frac{1}{2\mu} \right)\]
Again another image of fish will be formed H/2 below the mirror.
Real depth for that image of fish becomes H + H/2 = 3H/2
So, apparent depth from the surface of water = 3H/2μ
So, distance of the image from the eye
\[= \frac{H}{2} + \frac{3H}{2\mu} = H\left( 1 + \frac{3}{2\mu} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
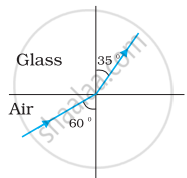 |
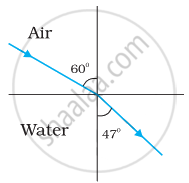 |
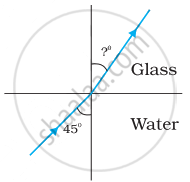 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.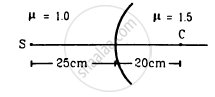
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
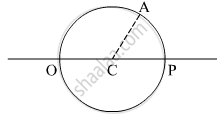
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
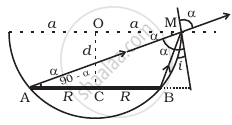
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
