Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
उत्तर
- Absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in the given medium.
- A stick or pencil kept obliquely in a glass containing water appears broken as its part in water appears to be raised.
- As the speed of light is different in two media, the rays of light coming from water undergo refraction at the boundary separating the two media.
- Consider the speed of light to be v in water and c in air. (Speed of light in air ≈ speed of light in vacuum)
∴ refractive index of water = `"n"_"w"/"n"_"a"="n"_"w"/"n"_"vacuum"="c"/"v"` - The relative refractive index of a medium 2 is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 and it is defined as the ratio of the speed of light v1 in medium 1 to its speed v2 in medium 2.
∴ The relative refractive index of medium 2,
1n2 = `"v"_1/"v"_2` - Consider a beaker filled with water of absolute refractive index n1 kept on a transparent glass slab of absolute refractive index n2.
- Thus, the refractive index of water with respect to that of glass will be,
gnw = `"n"_2/"n"_1=("c"/"v"_2)/("c"/"v"_1)="v"_1/"v"_2`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
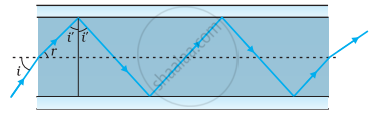
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
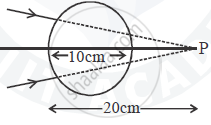
What is looming?
Write a note on optical fibre.
How does an endoscope work?
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
A ray of light passes through equilateral prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to `(3/4)^"th"` the angle of prism. The angle of deviation is ______.
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?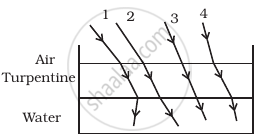
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
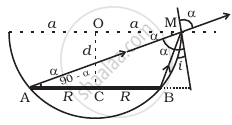
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
Using Huygen's wave theory, show that (for refraction of light):
`sin i/sin r = "constant"`
where terms have their usual meaning. You must draw a neat and labelled diagram.
