Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
उत्तर
Given,
Thickness of the glass slab, d = 2.1 cm
Refractive index, μ = 1.5
Shift due to the glass slab is given by,
\[∆ t = \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{\mu} \right) \right]d\]
\[= \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 5} \right) \right]\left( 2 . 1 \right)\]
\[= \frac{1}{3}\left( 2 . 1 \right) = 0 . 7 cm\]
Hence, the microscope should be shifted by 0.70 cm to focus the object 'P' again.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
A narrow beam of light passes through a slab obliquely and is then received by an eye following figure. The index of refraction of the material in the slab fluctuates slowly with time. How will it appear to the eye? The twinkling of stars has a similar explanation.
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
What is mirage?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
Light travels from an optically denser medium 'A' into the optically rarer medium 'B' with speeds 1.8 × 108 m/s and 2.7 × 108 m/s respectively. Then critical angle between them is ______.
(µ1 and µ2 are the refractive indices of media A and B respectively.)
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?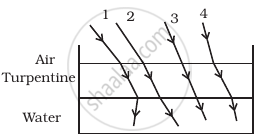
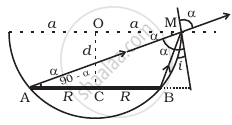
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
A convex lens made of material of refractive index 1.5 and having a focal length of 10 cm is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 3.0. The lens will behave as ______.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
