Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
उत्तर
Given,
Focal length of the convex lens, fd = 20 cm
Focal length of the concave lens, fc = 10 cm
Beam diameter of the incident light, d = 5.0 mm
Distance between both the lenses is 10 cm.
As per the question, the incident beam of light is parallel to the principal axis.
Let it be incident on the convex lens.
Now, let B be the focus of the convex lens where the image by the convex lens should be formed.
For the concave lens,
Object distance (u) = + 10 cm (Virtual object is on the right of concave lens.)
Focal length, fc = − 10 cm
Using the lens formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[\Rightarrow\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{- 10}+\frac{1}{+ 10}=\infty\]
\[\Rightarrow v=\infty\]
Thus, after refraction in the concave lens, the emergent beam becomes parallel.
As shown, in triangles XYB and PQB,
\[\frac{PQ}{XY} = \frac{RB}{ZB} = \frac{10}{20} = \frac{1}{2}\]
\[PQ = \frac{1}{2} \times 5 = 2 . 5 \text{ mm }\]
Thus, the beam diameter of the emergent light is 2.5 mm.
Similarly, we can prove that if the beam of light is incident on the side of the concave lens, the beam diameter (d) of the emergent light will be 1 cm.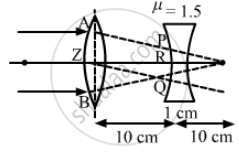
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
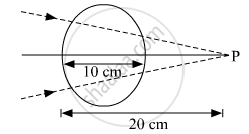
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
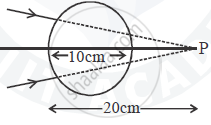
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
Why do stars twinkle?
What is Snell’s window?
How does an endoscope work?
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
Obtain the equation for lateral displacement of light passing through a glass slab.
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
Light travels from an optically denser medium 'A' into the optically rarer medium 'B' with speeds 1.8 × 108 m/s and 2.7 × 108 m/s respectively. Then critical angle between them is ______.
(µ1 and µ2 are the refractive indices of media A and B respectively.)
Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 108 ms−1 and 2.4 × 108 ms−1 respectively. Then the critical angle between them is:
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
