Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that for a material with refractive index `µ ≥ sqrt(2)`, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
उत्तर
Let the ray incident on face AB at angle i, after refraction, it travels along PQ and then interact with face AC which is perpendicular to the incident face.
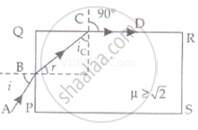
`u = 1/(sin i_c)` .....(Snell's law at c)
`Sin i_c 1/mu [sin i_c = 1/mu]`
`sin(90 - r) ≥ 1/mu` ......[∵ r + 90° + ic = 180]
`cos r ≥ 1/mu`
`cos^2 r ≥ 1/mu^2` ......(Squaring both sides)
`- cos^2 r ≤ 1/mu^2`
`1 - cos^2r ≤ 1 - 1/mu^2`
`sin^2r ≤ 1 - 1/mu^2` ......(I)
`sin i/sinr = mu` .....(By snell's law)
`sin i = mu sin r`
Or `sin^2i = mu^2 sin^2r` ......(Squaring both sides)
`1/mu^2 sin^2i = sin^2r` ......(II)
Put (II) in (I)
`1/mu^2 sin^2i ≤ 1 - 1/mu^2`
`sin^2i ≤ mu^2 - 1` ......[On multiplying by μ2 on both sides]
For smallest angle i.e., i = 90°
∴ `sin^2 90° ≤ mu^2 - 1` ......`[∵ mu ≤ sqrt(2)]`
`1 + 1 ≤ mu^2`
`2 ≤ mu^2`
Taking square root
`sqrt(2) ≤ mu` Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
What is looming?
Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of optical fiber.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
