Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
उत्तर
Given,
Thickness of the glass slab, d = 2.1 cm
Refractive index, μ = 1.5
Shift due to the glass slab is given by,
\[∆ t = \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{\mu} \right) \right]d\]
\[= \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 5} \right) \right]\left( 2 . 1 \right)\]
\[= \frac{1}{3}\left( 2 . 1 \right) = 0 . 7 cm\]
Hence, the microscope should be shifted by 0.70 cm to focus the object 'P' again.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
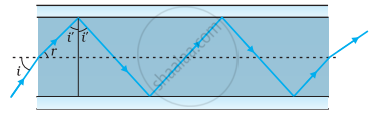
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

Figure shows a transparent hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm made of a material of refractive index 2.0. (a) A narrow beam of parallel rays is incident on the hemisphere as shown in the figure. Are the rays totally reflected at the plane surface? (b) Find the image formed by the refraction at the first surface. (c) Find the image formed by the reflection or by the refraction at the plane surface. (d) Trace qualitatively the final rays as they come out of the hemisphere.

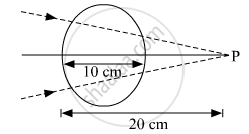
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
Why do stars twinkle?
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
How does an endoscope work?
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
A ray of light passes through equilateral prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to `(3/4)^"th"` the angle of prism. The angle of deviation is ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
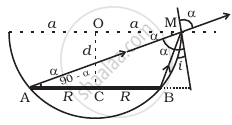
A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Figure). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index µ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?