Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A vessel contains water up to a height of 20 cm and above it an oil up to another 20 cm. The refractive indices of the water and the oil are 1.33 and 1.30 respectively. Find the apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above.
उत्तर
Given,
Height of water, dw = 20 cm
Height of oil, dO = 20 cm
The refractive index of the water (μw) = 1.33
The refractive index of oil (μO) = 1.30
Shift due to water is given by,
\[∆ t_w = 1 - \left( \frac{1}{\mu_w} \right) d_w\]
\[= \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 33} \right) \right]20\]
\[= \frac{1}{4}\left( 20 \right) = 5 cm\]
Shift due to oil,
\[∆ t_O = \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 3} \right) \right]20\]
\[ = 4 . 6 \text{ cm }\]
Therefore, total shift, Δt = 5 + 4.6 = 9.6 cm
Hence, apparent depth = 40 − (9.6) = 30.4 cm between the surface.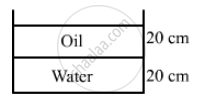
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
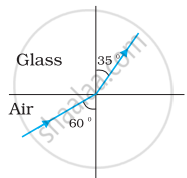
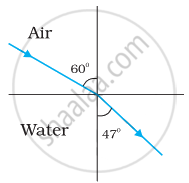
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
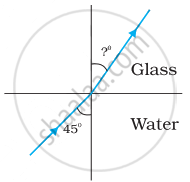 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm. The image will form at
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
Why do stars twinkle?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?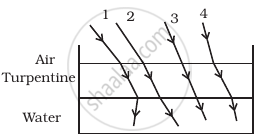
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
