Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

उत्तर
Given,
From the figure we can infer that the air is present in between the sheet, so it does not affect the shift. Therefore, the shift is only due to 3 sheets of different refractive indices, which is given by:
\[∆ t = \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_1} \right] t_1 + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_2} \right] t_2 + \left[ 1 - \frac{1}{\mu_3} \right] t_3\]
\[= \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{12} \right) \right]\left( 0 . 2 \right) + \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 3} \right) \right]\left( 0 . 3 \right) + \left[ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{1 . 4} \right) \right]\left( 0 . 4 \right)\]
= 0.2 cm
Hence, location of image of point P is located 0.2 cm above point P.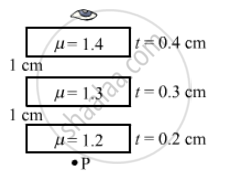
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
What is linearly polarized light?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.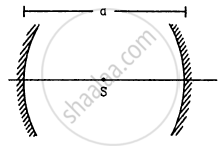
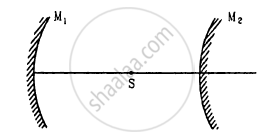
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
k transparent slabs are arranged one over another. The refractive indices of the slabs are μ1, μ2, μ3, ... μk and the thicknesses are t1 t2, t3, ... tk. An object is seen through this combination with nearly perpendicular light. Find the equivalent refractive index of the system which will allow the image to be formed at the same place.
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 5890 Å falls normally on a slit of width 0.2 mm. Find the distance between the first minima on the two sides of the central maximum of the diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed in the focal plane of a convex lens of focal length 50 cm. The lens is placed quite close to the slit.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because ______.
- light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
- there is no light scattered into this region.
- light is absorbed in this region.
- angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°.
