Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
उत्तर
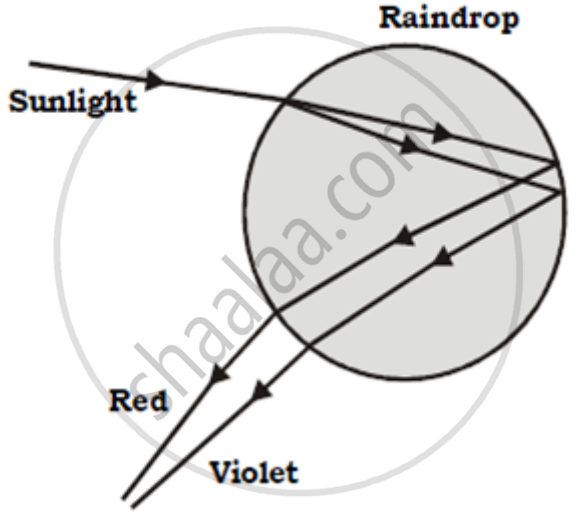
1. The beautiful phenomenon of the rainbow is a combination of different phenomena – dispersion, refraction, and reflection of light.
2. The rainbow appears in the sky after a rain shower.
3. The water droplets act as small prisms.
4. When sunlight enters the water droplets present in the atmosphere, they refract and disperse the incident sunlight.
5. Then they reflect it internally inside the droplet and finally again refract it.
6. As a collective effect of all these phenomena, the seven-colored rainbows are observed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Name the phenomenon responsible for it.
Why does unpolarised light from a source show a variation in intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel to its principal axis. As one moves away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis, the intensity of light
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.50) to water (μ = 1.33). Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
A point source is placed at a depth h below the surface of water (refractive index = μ). (a) Show that light escapes through a circular area on the water surface with its centre directly above the point source. (b) Find the angle subtended by a radius of the area on the source.
A container contains water up to a height of 20 cm and there is a point source at the centre of the bottom of the container. A rubber ring of radius r floats centrally on the water. The ceiling of the room is 2.0 m above the water surface. (a) Find the radius of the shadow of the ring formed on the ceiling if r = 15 cm. (b) Find the maximum value of r for which the shadow of the ring is formed on the ceiling. Refractive index of water = 4/3.
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Answer the following question in detail.
Is it possible to see primary and secondary rainbow simultaneously? Under what conditions?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
A plano-convex lens is made of material having refractive index 1.5. The radius of curvature of curved surface is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens is ____________ cm.
State any one difference between a primary rainbow and a secondary rainbow.
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
