Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
उत्तर
Using sign conventions, given,
Focal length of the concave mirror:
f = −20 cm
As per the question,
Magnification (m) is:
\[m = - \frac{v}{u} = 2\]
⇒ v = −2u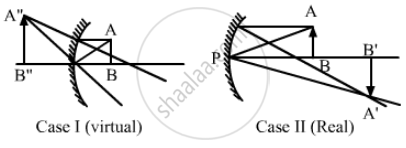
Case I (Virtual image):
Using mirror formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - \frac{1}{2u} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{3}{2u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u = \frac{3f}{2} = 30 \text{ cm }\]
Hence, the required positions of objects are 10 cm or 30 cm from the concave mirror.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Name the phenomenon responsible for it.
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friends is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height?
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f = 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. An eye is placed 60 cm to right of the lens and a distance h below the principal axis. The maximum value of h to see the image is
A candle flame 1.6 cm high is imaged in a ball bearing of diameter 0.4 cm. If the ball bearing is 20 cm away from the flame, find the location and the height of the image.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 5890 Å falls normally on a slit of width 0.2 mm. Find the distance between the first minima on the two sides of the central maximum of the diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed in the focal plane of a convex lens of focal length 50 cm. The lens is placed quite close to the slit.
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
Which of the following phenomena is prominently involved in the formation of mirage in deserts?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question : |
In an optical fibre, if n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, then which among the following, would be a correct equation?
| Case study: Mirage in deserts |
 |
|
To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object. Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called mirage. This type of mirage is especially common in hot deserts. Based on the above facts, answer the following question: |
The following figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fiber of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for the following phenomena to occur.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
