Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
Solution
Using sign conventions, given,
Focal length of the concave mirror:
f = −20 cm
As per the question,
Magnification (m) is:
\[m = - \frac{v}{u} = 2\]
⇒ v = −2u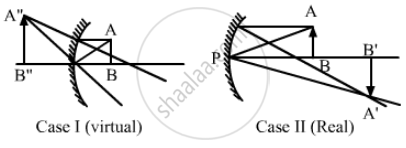
Case I (Virtual image):
Using mirror formula,
\[\frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow - \frac{1}{2u} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{3}{2u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u = \frac{3f}{2} = 30 \text{ cm }\]
Hence, the required positions of objects are 10 cm or 30 cm from the concave mirror.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
The image formed by a concave mirror
A concave mirror having a radius of curvature 40 cm is placed in front of an illuminated point source at a distance of 30 cm from it. Find the location of the image.
A concave mirror forms an image of 20 cm high object on a screen placed 5.0 m away from the mirror. The height of the image is 50 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.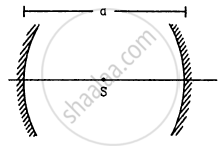
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

k transparent slabs are arranged one over another. The refractive indices of the slabs are μ1, μ2, μ3, ... μk and the thicknesses are t1 t2, t3, ... tk. An object is seen through this combination with nearly perpendicular light. Find the equivalent refractive index of the system which will allow the image to be formed at the same place.
An optical fibre (μ = 1.72) is surrounded by a glass coating (μ = 1.50). Find the critical angle for total internal reflection at the fibre-glass interface.
Light falls from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Find the angle of incidence for which the angle of deviation is 90°.
A point source is placed at a depth h below the surface of water (refractive index = μ). (a) Show that light escapes through a circular area on the water surface with its centre directly above the point source. (b) Find the angle subtended by a radius of the area on the source.
A paperweight in the form of a hemisphere of radius 3.0 cm is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer?
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
