Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A passenger in an aeroplane shall ______.
Options
never see a rainbow.
may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles.
may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric arcs.
shall never see a secondary rainbow.
Solution
A passenger in an aeroplane shall may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles.
Explanation:
As aeroplane is at higher altitude, the passenger in an aeroplane may see primary and secondary rainbow-like concentric circles.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
The image formed by a concave mirror
A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel to its principal axis. As one moves away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis, the intensity of light
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. Find the position or positions of an object for which the image-size is double of the object-size.
A point source S is placed midway between two converging mirrors having equal focal length f as shown in figure. Find the values of d for which only one image is formed.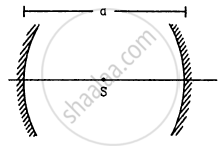
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ______ light.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 5890 Å falls normally on a slit of width 0.2 mm. Find the distance between the first minima on the two sides of the central maximum of the diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed in the focal plane of a convex lens of focal length 50 cm. The lens is placed quite close to the slit.
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
