Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel to its principal axis. As one moves away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis, the intensity of light
Options
remains constant
continuously increases
continuously decreases
first increases then decreases.
Solution
first increases then decreases
Since all beams of light are parallel to the principal axis, they will converge at the focus of a converging lens. Thus, the intensity of light increases till one reaches the focus and then starts decreasing as one moves beyond it.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blank:
Very fine particles mainly scatter ………… colored light.
Why can’t we see clearly through fog?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A convex lens is made of a material having refractive index
\[1 \cdot 2\] Both the surfaces of the lens are convex. If it is dipped into water (μ = 1.33), it will behave like
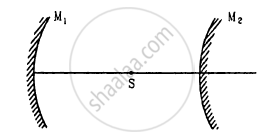
A converging mirror M1, a point source S and a diverging mirror M2 are arranged as shown in figure. The source is placed at a distance of 30 cm from M1. The focal length of each of the mirrors is 20 cm. Consider only the images formed by a maximum of two reflections. It is found that one image is formed on the source itself. (a) Find the distance between the two mirrors. (b) Find the location of the image formed by the single reflection from M2.
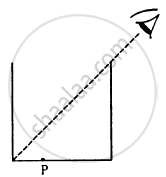
Locate the image of the point P as seen by the eye in the figure.

A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
A biconvex thick lens is constructed with glass (μ = 1.50). Each of the surfaces has a radius of 10 cm and the thickness at the middle is 5 cm. Locate the image of an object placed far away from the lens.
One end of a cylindrical glass rod (μ = 1.5) of radius 1.0 cm is rounded in the shape of a hemisphere. The rod is immersed in water (μ = 4/3) and an object is placed in the water along the axis of the rod at a distance of 8.0 cm from the rounded edge. Locate the image of the object.
The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 109 m and its distance from the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. Find the radius of the image of the sun formed by a lens of focal length 20 cm.
Explain: ‘How is a rainbow formed’?
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
